Smart security is a series of systems that use modern information technology means such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and big data to conduct all-round monitoring, early warning, prevention, control, and disposal of security prevention, aiming to improve the efficiency and accuracy of security prevention, thereby protecting people’s personal safety and property safety.
-
Security features
1) Intelligence: Automatically identify various safety hazards and dangerous factors, and issue early warnings and alarms in a timely manner.
2) Automation: Automatically take corresponding disposal measures to reduce manual intervention.
3) Efficiency: Improve the efficiency and response speed of security prevention.
4) Precision: Through big data and artificial intelligence technology, accurate monitoring and early warning can be achieved.
-
Security composition
1) Surveillance cameras: High-definition cameras are deployed in key areas to monitor and record activities in real time.
2) Intelligent video analysis: Identify abnormal behavior, object tracking, face recognition, etc. through video analysis technology.
3) Access control system: Use card swiping, fingerprint recognition, face recognition, etc. to control personnel entry and exit.
4) Intrusion alarm system: Includes door and window magnetic sensors, infrared detectors and other equipment to detect intrusions and trigger alarms.
5) Fire alarm system: Monitors smoke, flames and other signs of fire, and automatically triggers fire alarms.
6) Video access control intercom system: Combines video surveillance and intercom functions to ensure safe entry and exit management.
7) Electronic patrol system: Uses RFID or NFC technology to monitor and record patrol conditions in real time.
8) Emergency help button: Set at key locations for personnel to trigger alarms and help in emergencies.
-
Application Scenarios
1) Urban security management: used for public area monitoring, such as road traffic monitoring, urban monitoring center, etc.
2) Enterprise security: monitor the internal and external environment of the enterprise to ensure the safety of production equipment, property and employees.
3) Education: assist school administrators in monitoring campus safety and reduce campus bullying and adverse events.
4) Residential community and property management: improve the overall safety of the community and prevent criminal activities and illegal intrusions.
-
Product Introduction
-
Dynamic security monitoring


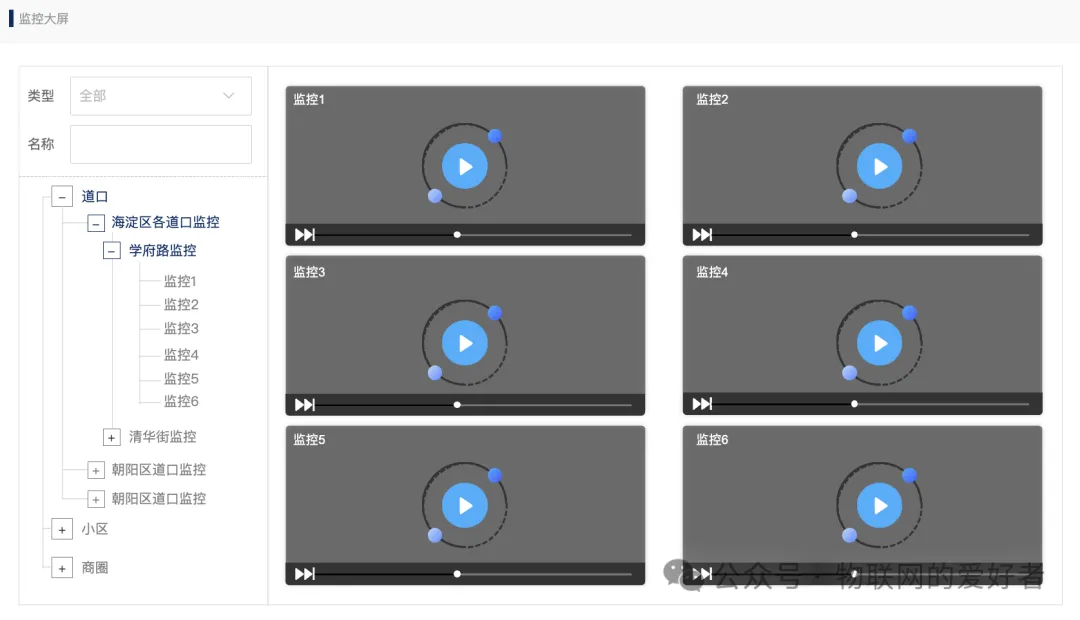
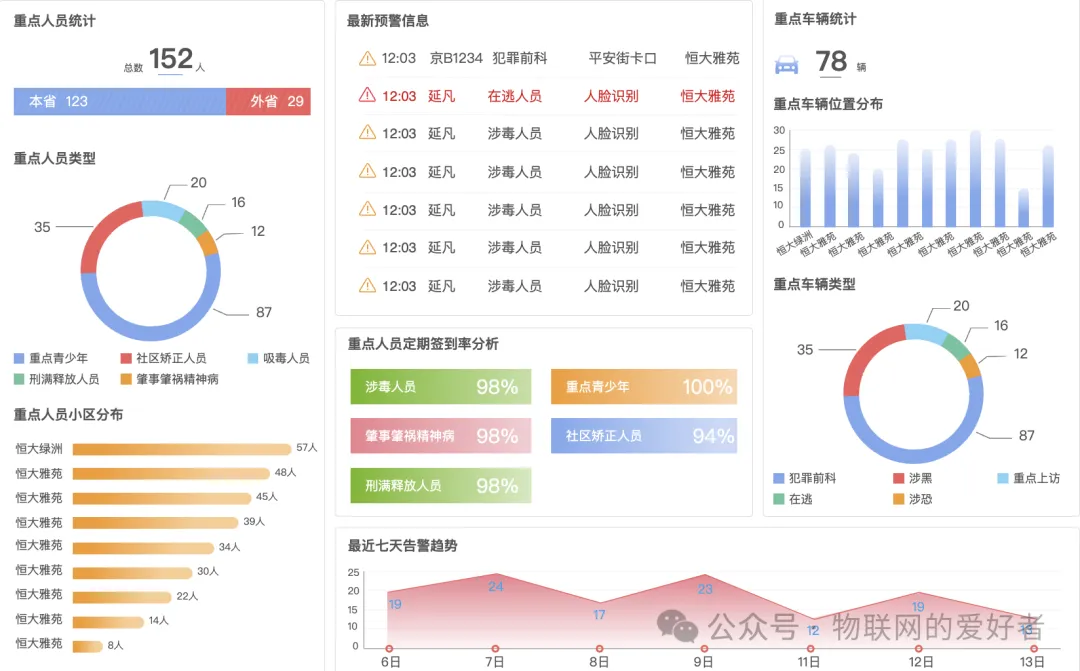
-
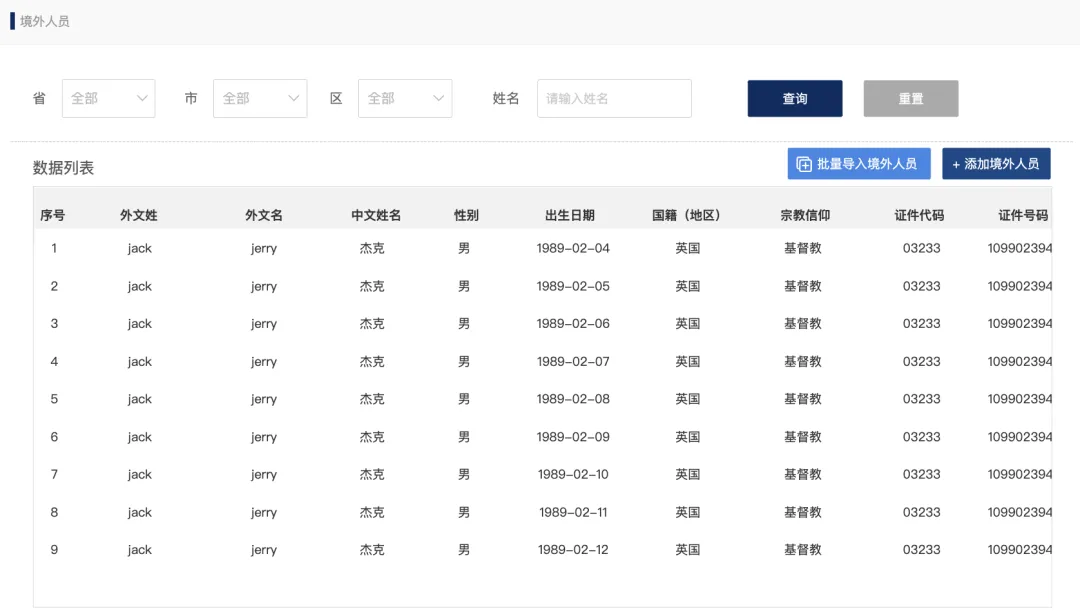
Personnel management
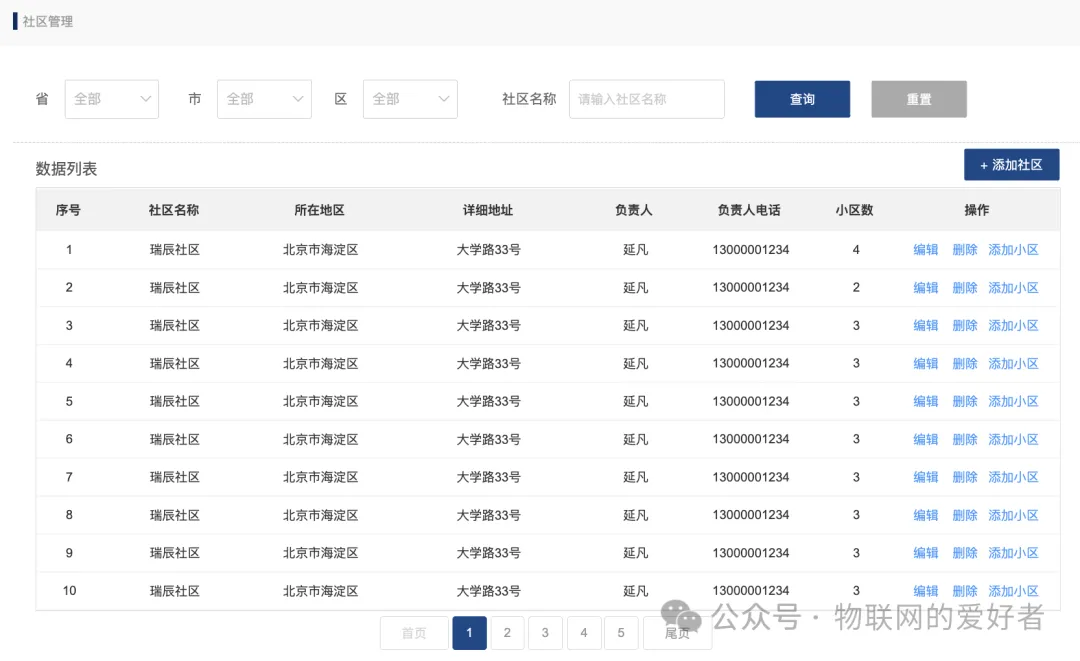
- Housing management
- Monitoring of key targets
